….With guests.
By Michael Shannon
“The Californians are an idle, thriftless people, and can make nothing for themselves. The country abounds in grapes, yet they buy, at a great price, bad wine made in Boston…” Richard Henry Dana, “Two Years Before the Mast.” 1830

Richard Henry Dana Jr. 1815-1882
Old Juan, the Mayordomo opened the door at the knock. Sitting their horses outside were Capitan Guillermo Dana and his wife Maria Josefa Petra Carrillo y Dana. Her children, 11 year old Maria Josefa and 4 year old William Charles rode the saddles of the Vaqueros carefully folded into the riders arms. Without dismounting, the Vaqueros bent down from the saddle and gently placed the ninos on their feet.
The patter of little feet was heard and then from between Old Juans legs squirted two little boys, Ramon Branch and his two year old little brother Leandro, called Roman. Barefoot in the dusty patio, they came to a sudden halt, delighted to greet the Dana children. Someone new to play with. La Dona Irelanda, Mrs Branch’s duena came bustling through the doorway, shooshing and fussing as she herded the children inside like a flock of little chickens, squawking and laughing all the way.
Behind them by the corrals were four of Don Guillermos Vaqueros led by Juan Medina. Dressed in their finest for the occasion in silk lined short jackets adorned with silver Conchos inlaid with jade or ivory buttons fastened with braided frogs. Each man sat his horse as if they were one with the animal. Their decorated and stamped California saddles were adorned with a large horn as large as a soup bowl. Each horse was reined with a beautifully braided Bosal noseband and jáquima. A well trained horse was ridden with almost no guidance from the Vaquero other than a little pressure on the noseband or his knees. Only women rode mares, no Vaquero would ever be seen astride anything other than a Stallion. Each Vaquero believed that they were the greatest horsemen that ever lived. Their spines were stiff with pride and the old saying that they wouldn’t walk across the courtyard on foot is true. A man astride believes his is as noble as any king.

They wore flat brimmed leather hats over silk bandanas, their long hair caught back in ponytails pomaded and shining. As they swung from their saddles their large roweled spurs rung with the sound of jingle bobs tinkling. Shaking out their best clothes, dusting them and arranging everything just so they turned and strode in their soft calf skin boots toward the Cocina never deigning to look back at the hosteler who was leading their horses into the corral. Immense pride in their own stature dripped from them like the morning dewdrops from an Oak.
Juan welcomed the Danas inside waving his arm in a generous sweep towards the host and hostess, Francisco Branch and his wife Manuela who stood in the great room of the newly completed grand hacienda. Manuela stepped forward to greet Josefa, still a stunning dark eyed beauty at 27. They shared an embrace and a brief soft kiss on each cheek as was the custom. Both women had been born and raised in Santa Barbara and were nearly the same age. A quarter century had passed since then and now they were Patronas and managed the households of their husbands vast rancho’s.
Manuela’s maid came forward and to take Josefas “Manton de Manila” but with a small wave of the hand Manuela bade her stay. She bent to look at her friends silk shawl with its elaborate embroidery and the long fringe on its edges, running her fingers along the fine silk from China. “Hermosa, preciosa,” she murmured, speaking in the language of Alta California. Arm in arm the two lovely young women turned to begin a tour of the newly completed home.

The rancheros shared an abrazo as was the custom in the land and walked outside to enjoy the view of the old Arroyo Grande from la Sala. The took their ease in chairs made by the Indians who worked on the rancho. Little Pedro the son of the cook presently arrived with a tray and two glasses which he promptly filled with wine made from the grapes originally grown by the Padres of mission San Luis Obispo de Tolosa and transplanted at Capitan Dana’s rancho Nipomo. Taking cigars from those offered by the servant they went through the process of lighting them. Dana leaned back and sent a stream of fragrant smoke skyward. commenting on the flavor. Branch said, “These Cigaros are hand rolled in the Phillipines and came by one of the trading ships just a few weeks ago. The long trip across the Pacifico doesn’t seem to have effected the quality, no?”
The two Don’s sat back and enjoyed their leisure time They were neither indolent or lazy as stated by the first white writers who came to California have stated. Each ran a vast Rancho of tens of thousands of acres. The Spanish word Don was not just an honorific but the description of a man whose literal fiefdom equalled the possession’s of European royalty. Each one was building a community of people dedicated to the advancement of not only their personal interests but the interest’s of their family and retainers.
The Hacienda was large and designed to shelter the family and the people who worked for them. The grist mill processed corn and oats to feed the many who depended on Francisco Branch. The clearing of the valley floor, which was ongoing provided growing ground for the many crops and the orchards which provided fruits and nuts to the establishment. Captain Dana did the same.
The conversation turned to spring. The spring roundup was approaching and the two men began discussing the organization needed to gather the wild cattle for counting and slaughter. The two men would work with the surrounding Hacendados to put together the Vaqueros, the skinners and the women who would scrape and process the cow hides for shipment. Camp sites, food, cooks, wood choppers and drivers for the carretas that would bring the hides out of the foothills and down to the ranch houses for storage until the ships such as the Alert, Pilgrim, Gypsy or the California of Tomas Robbins called at the cave landing to trade and load hides for shipment to the east coast. Thomas, “Don Tomas” Robbins who owned the Calera de Las Positas Rancho in Santa Barbara and the entirety of Santa Catalina island was Dana’s brother-in-law.

Capitan Guillermo Dana and Don Francisco Branch, both transplanted Yankees, one a sea captain and supercargo on ships trading between the California coast and New England, the other an American trapper and hunter who had come west with the William Wolfskill party of hunters in 1831. They both settled en La Puebla de Santa Barbara where they operated small stores and in Branch’s case, expeditions along the northern coast hunting otters and seals. Otter pelts were traded to the Russians stationed at Fort Ross. The Russian American fur company then sold the peltrie to the Chinese for up to one hundred dollars in the early 1800’s. Branch came in right at the end of the fur trade as most of the sea creatures had been hunted to near extinction by 1840. Although few actual coins were ever traded he built large savings of credits which he used to buy goods for his various enterprises. Though Branch had little education, he was a canny businessman and had come far since his arrival in Alta California.
Both men had converted to Catholicism and became Mexican citizens, married young girls from prominent Californio families and lobbied for grants from the governor of California. This was land confiscated from the Mission establishment when the Mexican government secularized the missions in 1833. The Mexican government confiscated the missions’ properties and exiled the Franciscan friars. The missions establishments were then broken up and their property was sold or given to private citizens. The land was intended to be returned to the Indians who had served the missions but politics reared it’s ugly head and the land was granted to prominent citizens. The Indians, neophytes as they were known lived in the old church buildings, the asistencias, or wherever they could find a place to stay. These Vista or Asistenecias were small mission settlements designed to extend the reach of the Missions at a much smaller cost. Don Francisco Branch was a neighbor of Jose Maria Teodoro Villavicencios who owned the Rancho Corral de Piedra which had two former mission properties, the Corral de Piedra and the smaller Canon Corralitos where the padres had once grazed their horses. from where the two Don’s sat they could look up the Corralitos which still held a portion of the Villavicencios horse herd.
The Arroyo Grande’s Santa Manuela, was in the center of a ring of ranchos. the Nipomo to the east, Francisco Quijado’s Bolsa de Chamisal to the south, and Jose Ortega’s Rancho Pizmo to the west. Neighbors nearby were Don Miguel Avila, Teodoro Avellanes on the Guadalupe and the Punta de Laguna of Luis Arellanes and Emigdio Miguel Ortega. Each one an easy ride by horseback. Visitors were frequent and hospitality demanded thats what is mine is yours. Visits could last for days and even weeks, especially amongst the women and children of the various ranchos.
Women and children learned to ride almost before they could walk. Californio women were nothing like the bonnet wearing side saddle riding women bedecked with ostrich plumes walking their horses through the parks of Manhattan, no, California women rode astride like men and from their earliest age they rode everywhere. Some could throw a reata as well as any Vaquero. Raised to be independent they were nobodies cupcakes. A braided quirt could quell the insolence of any man. Josefa Dana would have seen no need for a sidesaddle if there was ever such a thing in California. And if there was she would have ridden with the same elan as the men.*

At the Branch’s the crackling fireplaces warmed the rooms with old oak wood cut from the abundant coastal oak forests on the Santa Manuela Rancho. The smell of food being prepared in la cocina drifted on the afternoon breeze and added a fillip to the air where the Rancheros sat enjoying the days end.
Old Juan who wasn’t yet old but has been remembered in local lore as “Old Juan” and was Don Francisco Branch’s longest serving employee hustled out to supervise proper care of all the horses. The distances and the lack of roads of almost any kind meant the horses were the only form of transportation and were highly prized. The First horse in California escaped from the Portola expedition in 1770 and with the establishment of the mission system horses were brought up from Mexico and crossed with local wild stock. Padres and their Vaqueros were no less interested in horse breeding than anyone else . By the time of the Rancho era, crossbred Andalusians and arab Barbs numbered well over 25,000. Greater than the human population. Herds lived in semi-feral conditions in the foothills along the coastal areas where most of the ranchos were. Horse racing was a serious business in old California. Visitors remarked on the remarkable quality of California horses. They were so valuable that Captain Fremonts hare-brained attempt to annex California to the United States in 1846 that as his motley group of volunteers simply stole Captain Dana’s best horses in the dark of night, leaving his own worn out remuda and a note confiscating all the horses with a promissory note that could be redeemed for government cash. The only horse left was an old broodmare, to old and fat to ride.
Though there was no telegraph or any way of communicating with ranchos further south, Captain Dana sent a Vaquero to Guadalupe to warn Teodoro Avellanes that Fremont was coming and looking for mounts for his “Army.” Calling out his vaqueros, Don Teodoro made sure that there were no horses in sight when Fremont arrived. Forced to move on Fremonts group camped in the pouring rain at the north entrance of Foxen Canyon. Benjamin Foxen, another Yankee Ranchero was warned by another rider that the so-called army was headed his way. Meanwhile, Captain Dana and his Vaqueros were creeping up on the camp where the miserable, soaking wet Fremont “Army” was camped near todays town of Garey.
It was the practice in those days before fences that whenever a ranchero purchased a horse, he would tie an old broodmare to the new horse with a short rope. The two would run over the fields for a few days until they became fast friends. As a result, to the end of its life, no California horse would ever willingly desert his Caballada, something that neither Fremont nor his men were aware of.
Dana and the Vaqueros moved the broodmare around to where the evening breezes would blow her familiar scent to the grazing horses from Rancho Nipomo. With no warning a stampede began and before Fremont knew what was happening, Dana’s horses were racing across the fields, following their elderly broodmare back home to the ranch. Fremont’s men were once again reduced to marching by Shank’s Mare on their way southward toward the city of Santa Barbara.
The cook and her helpers worked in semi-outdoor kitchen (Cocina). Build with adobe walls about six feet high and a lean-to roof of Vigas closely spaced with smaller willow (El Mimbre) and a covering of reeds from the lower valley woven into thatch. It was almost completely waterproof. The three sided enclosure contained a Horno oven, a circle of stone for a pit fire and hanging above an iron try pot salvaged from a wrecked whaler. There was a small iron stove from a sailing ship with its stove pipe lifting the smoke and heat through the roof of the Cocina. The cooks worked in the building separated from the main house for good reason since fires were common in buildings that had wooden or thatched roofs. It would be a number of years before tile was made in enough quantity to roof the hacienda.
Hand made tables held clay bowls and utensils traded from the small coastal ships that unloaded imported goods and loaded hides at Cave Landing on Miguel Avilas ranch near the outlet of San Luis creek. Though isolated, Alta California benefited by long established trade with the far east.

The men moved inside and stood behind the elaborately carved chairs where their wives would sit. Furniture in the houses was made by the former neophytes who had been trained by the Padres at the mission since the late 18th century. The Chumash had been taught stock raising, agriculture. woodworking, masonry and all the chores required to run a household and since 1833 had been unemployed. For many who remained the ranchos offered near permanent employment. They had worked on every part of the Branch home.
The Chumash and the other Mission retainers who had stayed in the area built corrals, cleared the Monte’s and felled trees for building. Thousands of adobe brick were made by adding water and straw to the sticky adobe soil and then putting the black pudding into wooden molds and laid in rows in the sun to dry. All the old Haciendas were built this way with walls two and three feet thick.
Heated by small and narrow fireplaces where the wood cut from abundant trees was turned on end where it burned slowly. The small fireplaces were efficient and kept the Hacienda warm in winter. The heat generated soaked into the thick adobe walls and radiated back into the buiildings. It was a very efficient form of heating. In the summer the inside of the homes were cool because the thick walls which were shaded by trees stayed cool.

The Hacienda when it was owned by Francis Branch’s son Jose Frederico “Frank” Branch. 1860s
Seamstresses made clothes from imported fabric as well as the wool spun and woven from the sheep raised on the rancho. They made their own soap from the Lye obtained by pouring clean water through the abundance of wood ashes from the fireplaces. Lye was also used to flavor food and to keep insects off the corn crop. Tanning a cowhide requires lye. Mixing lye with animal fats makes soap. Lye will bleach cloth and is used in making paper. Curing meat, fish, fruits and vegetables requires lye. It’s also used to make dyes for fabric.
Both the Hacendados had orchards with apples, lemons, limes, pears, plums and oranges. All grown from cutting that came by pack horse from William Wolfskill’s horticultural nursery near Los Angeles, the first in California. Owned by the same man that Francis Branch came to California with. Both men demonstrated a variety of talent throughout their lifetimes.
Prepared in the cocina were plucked chickens hanging from hooks. Along one wall where irons skillets brought across the old Spanish trail by mountain men like Jed Smith for barter with merchants in Santa Fe or Taos found a ready market in California. Long pack trains of trade goods which would be traded for peltry and fresh horses for the return trip. Along the wall a shelf or two laden with fired clay pots of various sizes mixed with spoons, spatulas and the real treasure, a coffee grinder which had made the long trip from Mexico City to San Blas’s anchorage at Matanchen Bay and then north along the coast by ship.
Coffee had been introduced to the Sandwich islands in the 1820’s and was regularly traded with ships that called at the Hawaiian kingdom. Coffee trees had been introduced to America by Captain James Smith at Jamestown in 1723 and had spread quickly across the continent. Trading vessels could make the run from the islands to California in about three weeks weather permitting. In a single year, in the late thirties and early forties about 25 ships from the United states made the trip around Cape Horn to California. Averaging about 200 days, the small sailing vessels could pay for the cost of their building in single trip.
Economics of trade played a very important part of Hacienda life. With no manufacturing or commercial cities, anything that they needed had to be imported from Mexico or from abroad. The Spanish and Mexican governments tried to restrict trade to keep foreigners from settling in California and had enacted a 100% tariff in the 1790’s. All that achieved was to slow trade with Mexico proper and force the Californios to become active smugglers. The coastline was so long that there was literally no law enforcement and if there had been, the soldiers were easily bribed. They had families to feed too. The two thousand miles between Mexico City and Alta California was a formidable barrier.
To the uninformed 18 year old Yankee, Richard Henry Dana, Alta California seemed backward, the population ignorant and he clearly looked down on the Californios. What he missed is that California was part of one of the oldest worldwide trade routes that ever existed.
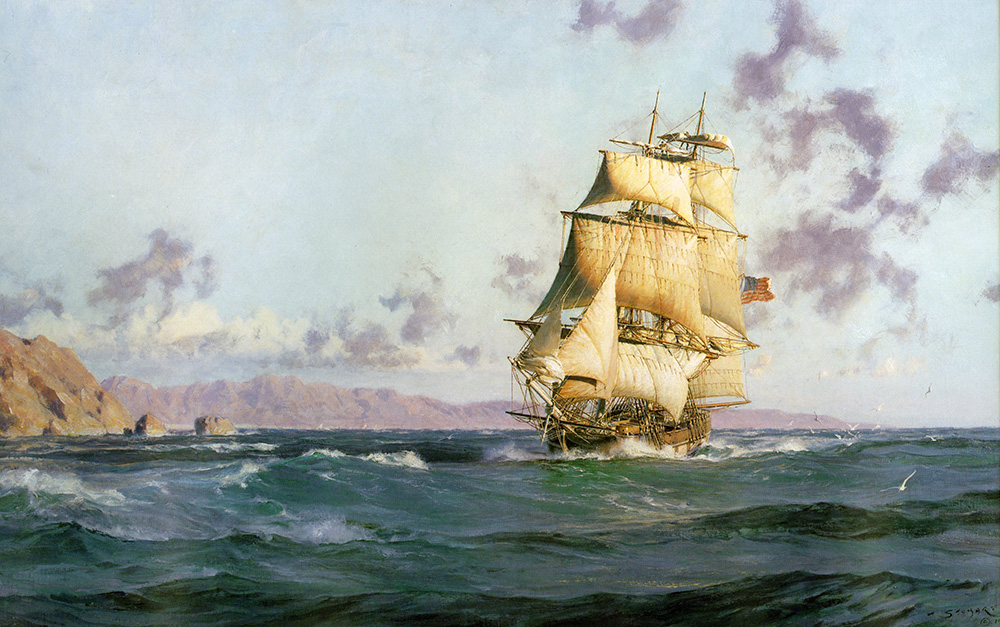

The Brig Pilgrim, 86′ foot at waterline and a 21 foot beam Leaving Monterey Bay. 1834
The famous silver fleet or plate fleet; from the Spanish: plata meaning “silver”, was a convoy system of sea routes organized by the Spanish Empire from 1566 to 1790, which linked Spain with its territories in the Americas across the Atlantic. The convoys were general purpose cargo fleets used for transporting a wide variety of items, including agricultural goods, lumber, various metal resources such as silver and gold, gems, pearls, spices, sugar, tobacco, silk, and other exotic goods from Spains overseas territories of the Spanish Empire to the Spanish mainland. Spanish goods such as oil, wine, textiles, books and tools were transported in the opposite direction.
The West Indies fleet was the first permanent transatlantic trade route in history. Similarly, the related Manila galleon trade was the first permanent trade route across the Pacific. The Spanish West and East Indies fleets are considered among the most successful naval operations in history and, from a commercial point of view, they made possible the key components of today’s global economy.
The Manila galleons mostly carried cargoes of Chinese and other Asian luxury goods in exchange for New World silver. Silver prices in Asia were substantially higher than in America, leading to an arbitrage opportunity for the Manila galleon. Every space of the galleons were packed tightly with cargo, even spaces outside the holds like the decks, cabins, and magazines. In extreme cases, they towed barges filled with more goods. While this resulted in slow passage that sometimes resulted in shipwrecks or turning back, the profit margins were so high that it was commonly practiced. These goods included Indian ivory and precious stones, Chinese silk and porcelain, cloves from the Moluccas islands, cinnamon, ginger, lacquers, tapestries and perfumes from all over Asia. In addition, slaves, collectively known as “chinos” from various parts of Asia, mainly slaves bought from the Portuguese slave markets and Muslim captives from the Spanish–Moro conflict were also transported from the Manila slave markets to Mexico. Free indigenous Filipinos also migrated to Mexico via the galleons where the crews would jump ship. These men comprised the majority of free Asian settlers the “chinos libres” in Mexico, particularly in regions near the terminal ports of the Manila galleons, San Blas and Acapulco. The route also fostered cultural exchanges that shaped the identities and the culture of all the countries involved.
In an age where time was measured differently, the long voyages or transportation times to get goods from Spain or the Phillipines to the Branch’s rancho was simply a factor that the Hacendado’s calculated.
The cooks in the kitchen didn’t care. They served Francis Branch and the where and the when of goods came from was of no matter. Their job was the feeding of the family and its retainers.
Red peppers, green peppers, dried tomatoes, garlic flowers, bay leaves, all strung together in multicolored bunches hung from a wrought iron rack hung in the corner of the room over a heavy table where the two cooks stood working. The older Mexican ladies from Sonora showed that the speed at which they worked belied had little to do with their ample size. They chattered with a sinuous melodious stream of Spanish mixed with Chumash and an occasional English word as they worked, laughing and teasing, especially the two little part Chumash girls that were the scullery maids. Laughter always made the food taste better they said. The little brown boy who swept the hard packed floor scuttled about trying to avoid the gentle kicks aimed at him when he got underfoot.

Chubby fingers flashed and the home ground and mixed flour from the Branch mill hung in the air as they rolled the batter into little balls, twirling and patting tortillas into shape with a staccato rhythm that mimicked the tattoo of little drums.
Bubbling over the fire, a pot of frijoles de olla and another of carne con chile steeped. Stores of wheat, beans, lentils and dried vegetables and fruit were stored in finely woven Chumash made baskets some so tightly made they would hold water. Some baskets had woven covers some were covered by a piece of wood with a small stone to keep out the mice who were everywhere in this little rodents paradise.

Dried salmon from the creek, fish from the reef and open sea along with dressed rabbit hung from the vigas overhead. Clay jars of salt, peppercorn, dried onions and lentils plucked from the creek banks sat on shelves with native California beans like Lima beans, butter and black-eyed beans along with both dark and light kidney beans, cranberry beans and heaps of wild blackberries gathered in the valley floor where armed Vaqueros protected the pickers from the numerous grizzly bears who also laid claim to the bounty.
From the Hacienda on its hill it was less than a mile to the bear pit where Branch and his vaqueros regularly caught and killed the monsters. The bears could and did carry off entire steers and other livestock. There were yet parts of the valley floor where no man went. Down the valley on the El Pizmo the swampy monte was so dense as to be impassable by man or horse, but not the Grizzly. Choked with wild berries it was exactly to the taste of the bears.

The valley was a paradise, the soil so rich that it was said if you threw a rock on it, it would grow pebbles.
As the sun fell towards dusk, the dinner bell began to clang from the Cocina, where the cook and her helpers were preparing to serve. The boy came out onto La Sala and murmured that La Cena Familiar was being brought in by the young women who served the cook for she was responsible for feeding nearly everyone on the Rancho. As the women were seated, servants brought out the meal.
The men had seated the women and then pulled out their own chairs and sat. The other guests took their places, before the door opened, the savory smell of food drifted into the room. Backing through the door the cooks laid on the table the big pot of Frijoles de Olla, red beans cooked with red chiles, wild onions from the creek, next a platter of chicken, breaded with crumbs from baked tortillas. This was followed by Squash blossom fritters garnished with salt, and wild sage gathered from the hillsides around the Hacienda then sprinkled with goat cheese made from the Rancho’s goat herd. A Chinese tureen filled with vegetable soup made from potatoes, carrots, wild leeks, onion, chopped cabbage from the kitchen garden and then sprinkled with ground red pepper. A pot of pumpkin soup arrived, an old Chumash recipe made from sliced and cubed pumpkin, sliced leeks, chicken broth, cows butter and pepper. The butter was something the Chumash didn’t have but served as examples of the blending of different cultures. The main dish which came in last was on a large figured platter brought from China. White porcelain with indigo blue figures it was heaped with braised short ribs smothered in onions, carrots, celery potatoes, parsley and sage. Each rib swimming in a sauce made from the Mission grapes and Brandy from the Calvados region of France. Crossing the Atlantic Ocean to Vera Cruz, Mexico and carried by pack train and wagon, the bottle had made the journey to California.
A heaping dish of fresh made tortillas, rolled and eaten as a compliment to the meal was laid out. Each of the adults ate from imported china which came east across the Pacific from the Philippines and glass goblets made in the city of Puebla, Mexico. Napkins of the finest embroidered linen were at each place setting. Sugar horns from the Sandwich Islands and bowls of pepper and salt were scattered about.
When the meal was complete the brandy was served for the men and Sherry for the women. At each place setting the servants laid a tortilla rolled with chocolate inside as a savory.
The guests at the table represented the variety of Californio peoples. The host was an American from Scipoio, New York. His principal guest, Captain William Dana a Bostonion. Their wives, both from Santa Barbara, the center of Californias largest pueblo, both from prominent families who had lived in Alta California since its founding. Mrs Branch’s sister Maria was married to Michael Price who owned El Rancho Pizmo. Price was from Bristol, England. The Priest who gave the blessing was a Spaniard educated in a Franciscan university in Europe, the Vaqueros were mostly Chumash or descendants of mixed marriages. The current term mestizo was rarely used in mission records: more common terms were indio, europeo, mulato, coyote, castizo, and other caste terms for someone of mixed breed. Some of them were of Indian and Spanish blood or from the Chumash or other native tribes. The chief cook was Chinese, lured from a transpacific trader and at least one vaquero, a Kanaka from the Sandwich Islands.
The Californios were neither indolent nor backward. Francis Branch had a school in his home for his own and the children of the men and women who worked for him. His account books, along with William Danas are part of the historical record. The descendants of those families live in and about San Luis Obispo county to this day. Their legacy exists in the names of streets, schools and their extended families. They were pioneers in every sense of the word and they made the world we live in today.
Richard Henry Dana was wrong.
“Were the devil himself to call
for a night’s lodging, the
Californian would hardly find
it in his heart to bolt the door…”
Diary of
Walter Colton
Monterey, 1850

The old Branch Adobe Hacienda about 1860. Branch Mill Road in foreground.
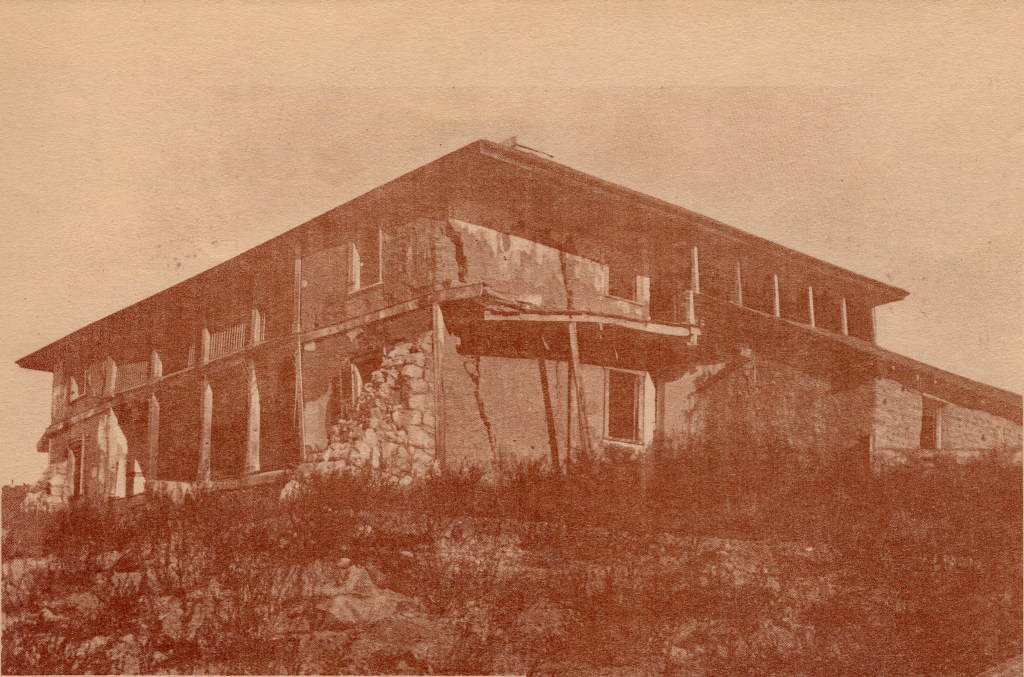

The old Branch home in 1887, slowly melting away. It is completely gone now.
*With the flood of Easteners during the gold rush, mores changed and sidesaddles became de riguer for women. Still, on the ranches women and girls persisted in the old practice of riding astride. My own great-grandmother shocked the staid gentry of Santa Barbara by doing just that in the first La Fiesta parade in 1924. Born and raised on the old San Juan Canon de Santa Ana Rancho she was not one to care what anyone thought. She was admired in the family for her independence.
Michael Shannon grew up on the old Rancho Santa Manuela about a mile from the original Hacienda. He went to Branch Elementary school and knows many of the Branch descendants. Many of the Branch grandchildren were still alive when he was a boy. Stories abound.